
After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Each account has its own ledger, and all the ledgers are kept in a central location called the ledger room. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
Tangible Real Accounts
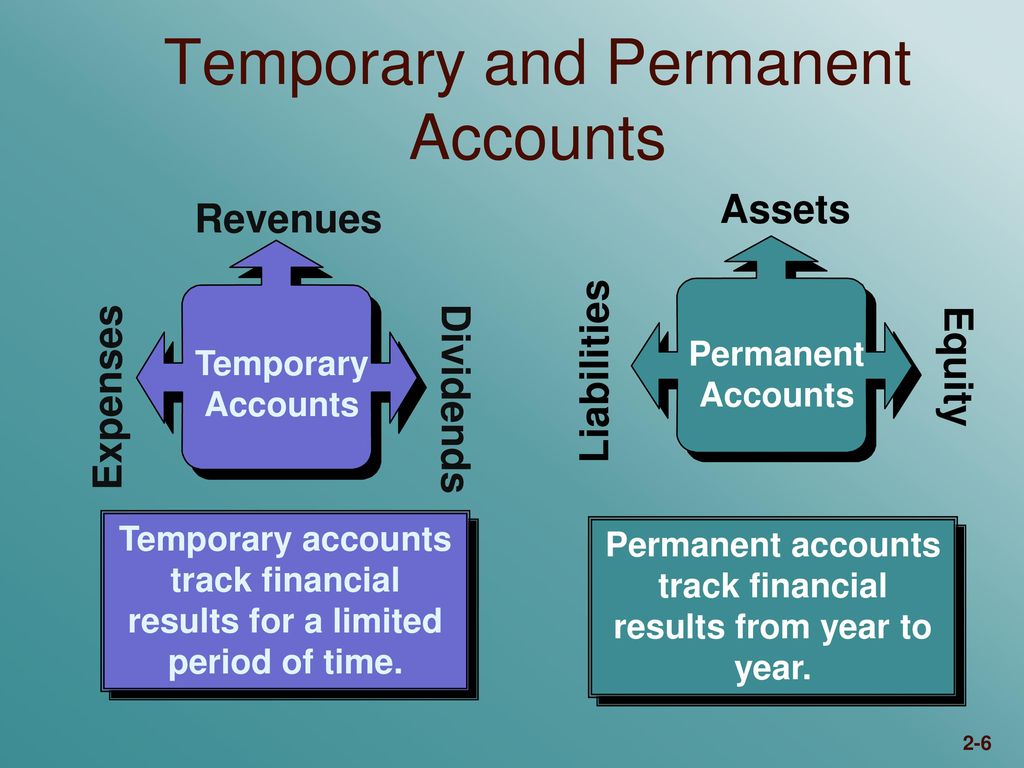
They include asset accounts, liability accounts, and capital accounts. Before you can learn more about temporary accounts vs. permanent accounts, brush up on the types of accounts in accounting. The company’s revenue for the financial year 20X2 is $800 million and its expenses are $600 million.
How Liam Passed His CPA Exams by Tweaking His Study Process
When a company issues common stock, it is essentially selling a piece of ownership in the business to investors. A debit entry increases an asset account or decreases a liability or equity account, while a credit entry decreases an asset account or increases a liability or equity account. T-accounts are used to represent ledger accounts in a simplified form.
Efficiency in closing periods
It can be used to fund operations, invest in new projects, or pay off debt. By managing their capital effectively, businesses can ensure that they have the resources they need to grow and succeed. The cash flow statement shows the inflow and outflow of cash from a company’s operations, investing activities, and financing activities.
To manage customer accounts effectively, businesses need to keep accurate records of customer transactions and maintain open lines of communication with customers. This account is used to track money owed to the business by customers who have not yet paid for goods or services. There are certain rules that govern the use of debits and credits in accounting.
- Expense accounts are a type of account used to track the expenses of a business.
- Accrued revenue—an asset on the balance sheet—is revenue that has been earned but for which no cash has been received.
- Inconsistent accounting practices can also lead to challenges in managing temporary and permanent accounts.
- Income summary effectively collects NI for the period and distributes the amount to be retained into retained earnings.
- At the end of the year, its ending balance is shifted to a different account, ready to be used again in the next fiscal year to accumulate a new set of transactions.
These accounts include accounts of individuals such as attorneys, executors, and so on. This is the main difference between permanent and temporary accounts. Automation simplifies the reconciliation process for both temporary and permanent accounts. Automated reconciliation tools compare account balances against external statements or records, ensuring that discrepancies are identified and resolved efficiently. Automation tools often include features for detecting and correcting errors in real-time.
If at the end of 2020 the company had Cash amounting to $100,000, that amount will be carried as the beginning balance of cash in 2021. If cash increased by $50,000 during 2021, then the ending balance would be $150,000. Read on to learn the difference between temporary vs. permanent accounts, examples of each, and how they impact your small business. which of the following accounts are permanent An adjusting journal entry occurs at the end of a reporting period to record any unrecognized income or expenses for the period. Now that you know more about temporary vs. permanent accounts, let’s take a look at an example of each. Finally, if a dividend was paid out, the balance is transferred from the dividends account to retained earnings.
Ledger accounts are used to record transactions related to personal accounts. A ledger is a book or a computer program that contains a complete record of all the transactions that have been made in an account. Personal accounts are accounts that represent individuals or organizations with whom the company has a financial relationship. In accounting, you deal with a variety of accounts to balance and organize your books. Let’s say you have a cash account balance of $30,000 at the end of 2021.
A nominal account, or temporary account, is essentially the opposite of a real account in accounting. Your real accounts reflect your company’s financial status and can change from period to period because they’re active throughout the entire year. Your year-end balance would then be $55,000 and will carry into 2023 as your beginning balance. This permanent account process will continue year after year until you don’t need the permanent accounts anymore (e.g., when you close your business). Because you don’t close permanent accounts at the end of a period, permanent account balances transfer over to the following period or year.
Some examples of nominal accounts include rent expense, insurance expense, cost of goods sold, repairs, wages payable, service revenue, and interest revenue. These accounts are used to record transactions that are related to the operation of a business. Permanent accounts carry the ending balances of the balance sheet to the beginning of the next year.
